Chemical Formula Of Sodium Oxide
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name Sodium oxide | |||
| Other names Disodium oxide | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| CAS Number |
| ||
| 3D model (JSmol) |
| ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.013.827 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| PubChem CID |
| ||
| UNII |
| ||
| Un number | 1825 | ||
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
| ||
| InChI
| |||
| SMILES
| |||
| Properties | |||
| Chemical formula | Na two O | ||
| Molar mass | 61.979 one thousand·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | white solid | ||
| Density | 2.27 1000/cmiii | ||
| Melting point | i,132 °C (2,070 °F; 1,405 Thousand) | ||
| Boiling indicate | 1,950 °C (iii,540 °F; 2,220 Chiliad) sublimates | ||
| Sublimation | sublimates at 1275 °C | ||
| Solubility in water | Reacts to grade NaOH | ||
| Solubility | Reacts with ethanol | ||
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | −19.8·10−6 cm3/mol | ||
| Structure | |||
| Crystal structure | Antifluorite (face centered cubic), cF12 | ||
| Infinite group | Fm3one thousand, No. 225 | ||
| Coordination geometry | Tetrahedral (Na+); cubic (O2−) | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
| Heat chapters (C) | 72.95 J/(mol·K) | ||
| Std molar | 73 J/(mol·K)[i] | ||
| Std enthalpy of | −416 kJ/mol[1] | ||
| Gibbs free energy (Δf One thousand ⦵) | −377.ane kJ/mol | ||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safe and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
| Main hazards | corrosive, reacts violently with water | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
| Pictograms |  [ii] [ii] | ||
| Hazard statements | H314 | ||
| Precautionary statements | P260, P264, P280, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P363, P405, P501 | ||
| NFPA 704 (burn diamond) | 3 0 ane | ||
| Flash point | non-flammable | ||
| Safety data canvass (SDS) | ICSC 1653 | ||
| Related compounds | |||
| Other anions | Sodium sulfide Sodium selenide Sodium telluride Sodium polonide | ||
| Other cations | Lithium oxide Potassium oxide Rubidium oxide Caesium oxide | ||
| Related sodium oxides | Sodium peroxide Sodium superoxide Sodium ozonide | ||
| Related compounds | Sodium hydroxide | ||
| Except where otherwise noted, information are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). Infobox references | |||
Sodium oxide is a chemical compound with the formula Na2O. It is used in ceramics and glasses. It is a white solid but the compound is rarely encountered. Instead "sodium oxide" is used to describe components of various materials such equally glasses and fertilizers which incorporate oxides that include sodium and other elements.
Construction [edit]
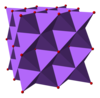
The structure of sodium oxide has been adamant by X-ray crystallography. About alkali metallic oxides Thousand2O (One thousand = Li, Na, K, Rb) crystallise in the antifluorite structure. In this motif the positions of the anions and cations are reversed relative to their positions in CaF2, with sodium ions tetrahedrally coordinated to 4 oxide ions and oxide cubically coordinated to 8 sodium ions.[3] [4]
Preparation [edit]
Sodium oxide is produced by the reaction of sodium with sodium hydroxide, sodium peroxide, or sodium nitrite:[5]
- ii NaOH + ii Na → 2 NaiiO + Htwo
To the extent that NaOH is contaminated with h2o, correspondingly greater amounts of sodium are employed. Excess sodium is distilled from the crude product.[half-dozen]
A second method involves heating a mixture of sodium azide and sodium nitrate:[vi]
- 5NaN3 + NaNO3 → 3NatwoO + 8Due north2
Called-for sodium in air produces a mixture of Na2O and sodium peroxide (Na2O2).
Applications [edit]
Glassmaking [edit]
Glasses are often described in terms of their sodium oxide content although they do not really contain Na2O. Furthermore, such spectacles are not made from sodium oxide, only the equivalent of Na2O is added in the form of "soda" (sodium carbonate), which loses carbon dioxide at high temperatures:
- Na2CO3 → Na2O + COtwo
- Na2O + SiO2 → NaiiSiO3
- NaiiCO3 + SiO2 → NatwoSiOiii + CO2
A typical manufactured glass contains around fifteen% sodium oxide, 70% silica (silicon dioxide), and 9% lime (calcium oxide). The sodium carbonate "soda" serves as a flux to lower the temperature at which the silica mixture melts. Such soda-lime glass has a much lower melting temperature than pure silica and has slightly higher elasticity. These changes ascend because the Na2[SiO2]x[SiO3]-based material is somewhat more than flexible.
Reactions [edit]
Sodium oxide reacts readily and irreversibly with water to give sodium hydroxide:
- NatwoO + HtwoO → ii NaOH
Considering of this reaction, sodium oxide is sometimes referred to as the base anhydride of sodium hydroxide (more archaically, "anhydride of caustic soda").
References [edit]
- ^ a b Zumdahl, Steven Due south. (2009). Chemical Principles 6th Ed. Houghton Mifflin Company. p. A23. ISBN978-0-618-94690-7.
- ^ Sigma-Aldrich Co., Sodium oxide. Retrieved on 2014-05-25.
- ^ Zintl, E.; Harder, A.; Dauth B. (1934). "Gitterstruktur der oxyde, sulfide, selenide und telluride des lithiums, natriums und kaliums". Z. Elektrochem. Angew. Phys. Chem. forty (8): 588–93. doi:x.1002/bbpc.19340400811. S2CID 94213844.
- ^ Wells, A. F. (1984) Structural Inorganic Chemistry, Oxford: Clarendon Press. ISBN 0-19-855370-6.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN978-0-08-037941-8.
- ^ a b E. Dönges (1963). "Sodium Oxide (IV)". In G. Brauer (ed.). Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd Ed. Vol. 1pages=975-6. NY,NY: Academic Press.
Chemical Formula Of Sodium Oxide,
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sodium_oxide
Posted by: wilsonceshounce72.blogspot.com




0 Response to "Chemical Formula Of Sodium Oxide"
Post a Comment